▼
Anatomy
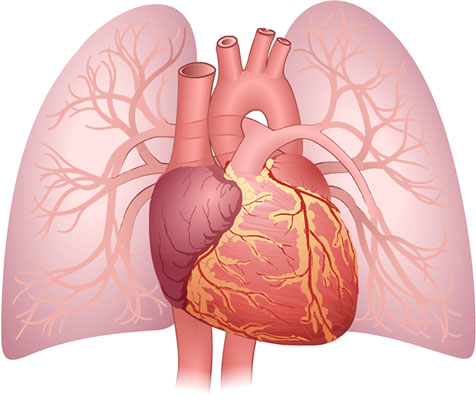
Right
Left
Anatomy Outside
To understand how the heart works, it is important to know the names of the parts of the heart and what they do. This section shows where the parts of the heart are and describes what they do.
Select the name of the part of the heart or blood vessel from the list below to see a picture and a description of what it does.
Press the “SHOW INSIDE” button to show the inside of the heart.
Aorta

Aorta: The largest artery in the body. The aorta carries oxygen-rich blood away from the heart, to the rest of the body.
Arteries to Head and Arms

Arteries to Head and Arms: The brachiocephalic trunk, the left common carotid artery, and the left subclavian artery carry blood upwards.
Atrium (Left)
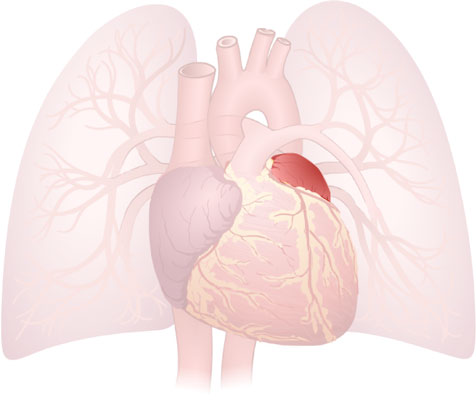
Atrium (Left): Thin-walled upper chamber of the heart that receives oxygenated blood from the lungs.
Atrium (Right)
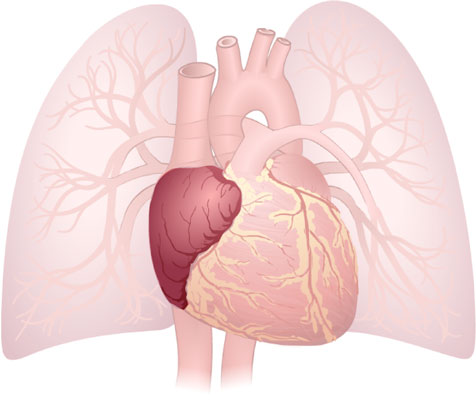
Atrium (Right): Thin-walled upper chamber of the heart that receives deoxygenated blood from the rest of the body.
Inferior Vena Cava
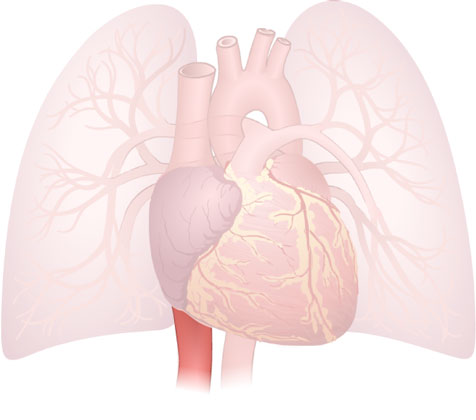
Inferior Vena Cava: A large vein that delivers deoxygenated blood from the lower body into the heart.
Lungs

Lungs: Structures that inflate and deflate with air just like balloons. Everyone has 2 lungs, left and right. In the lungs, carbon dioxide travels from the blood to the air and oxygen travels from the air to the blood.
Pulmonary Arteries
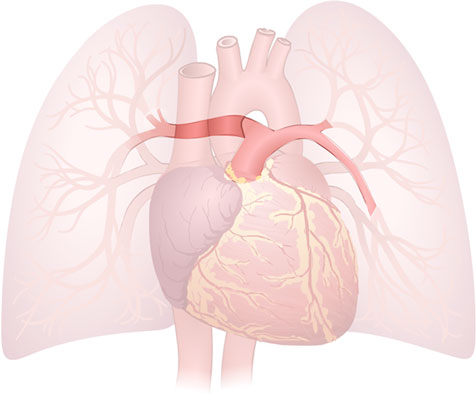
Pulmonary Arteries: Blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
Superior Vena Cava
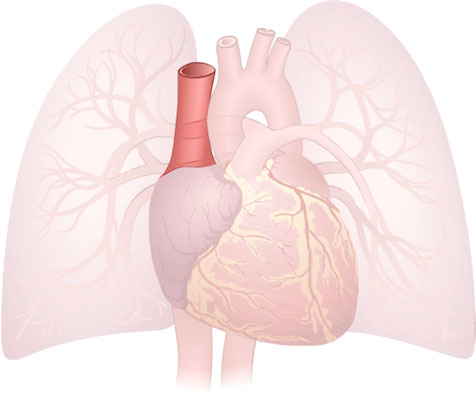
Superior Vena Cava: A large vein that delivers deoxygenated blood from the upper body into the heart.
Ventricle (Left)

Ventricle (Left): Lower chamber of the heart that pumps deoxygenated blood into the lungs. The right ventricle has thinner walls than the left ventricle.
Ventricle (Right)
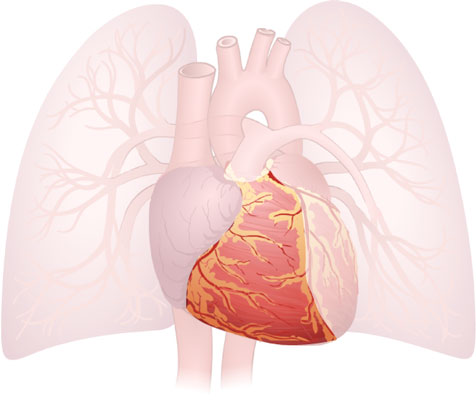
Ventricle (Right): Lower chamber of the heart that pumps oxygenated blood to the body. The left ventricle has thicker walls than the right ventricle.

Right
Left
Anatomy Inside
To understand how the heart works, it is important to know the names of the parts of the heart and what they do. This section shows where the parts of the heart are and describes what they do.
Select the name of the part of the heart or blood vessel from the list below to see a picture and a description of what it does.
Press the “SHOW OUTSIDE” button to show the outside of the heart.
Aorta

Aorta: The largest artery in the body. The aorta carries oxygen-rich blood away from the heart, to the rest of the body.
Aortic Valve

Aortic Valve: 3-leafed valve that prevents blood from flowing backwards from the aorta into the left ventricle.
Arteries to Head and Arms
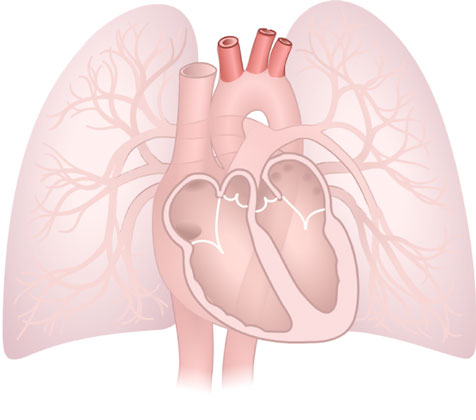
Arteries to Head and Arms: The brachiocephalic trunk, the left common carotid artery, and the left subclavian artery carry blood upwards.
Atrium (Left)

Atrium (Left): Thin-walled upper chamber of the heart that receives oxygenated blood from the lungs.
Atrium (Right)
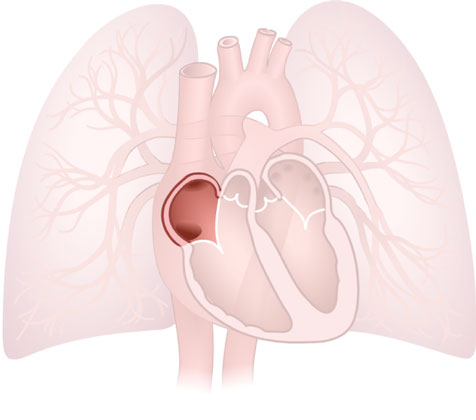
Atrium (Right): Thin-walled upper chamber of the heart that receives deoxygenated blood from the rest of the body.
Inferior Vena Cava
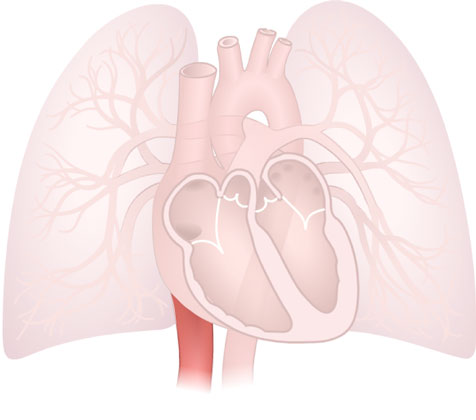
Inferior Vena Cava: A large vein that delivers deoxygenated blood from the lower body into the heart.
Lungs

Lungs: Structures that inflate and deflate with air just like balloons. Everyone has 2 lungs, left and right. In the lungs, carbon dioxide travels from the blood to the air and oxygen travels from the air to the blood.
Mitral (Bicuspid) Valve
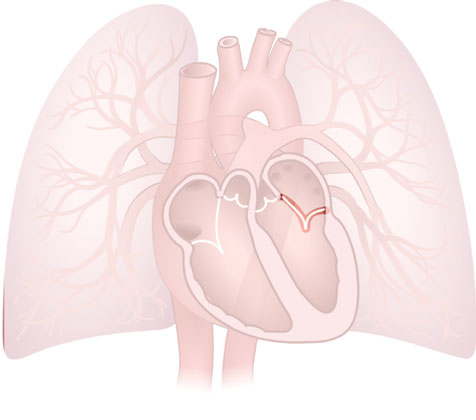
Mitral (Bicuspid Valve): 2-leafed valve that prevents blood from flowing backwards from the left ventricle into the left atrium.
Pulmonary Arteries
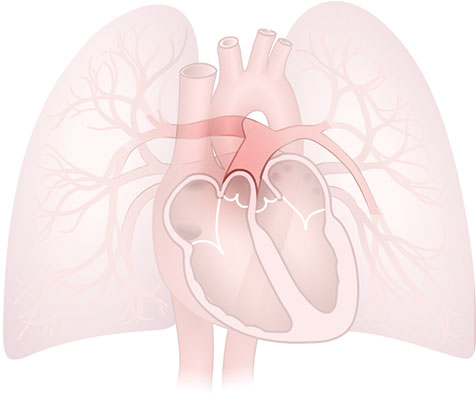
Pulmonary Arteries: Blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
Pulmonary Valve
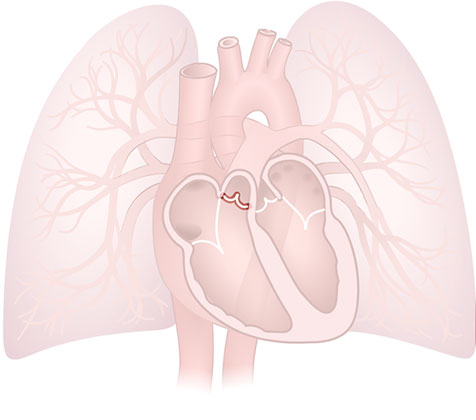
Pulmonary Valve: 3-leafed valve that prevents blood from flowing backwards from the pulmonary artery into the right ventricle.
Pulmonary Veins
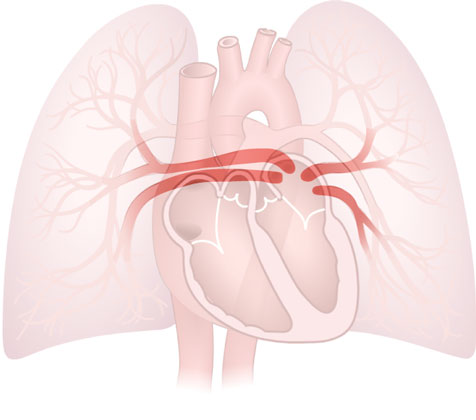
Pulmonary Veins: Blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
Septum
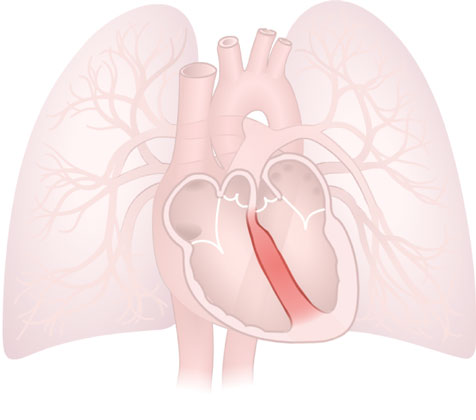
Septum: The thin wall that separates the right side of the side of the heart from the left side.
Superior Vena Cava
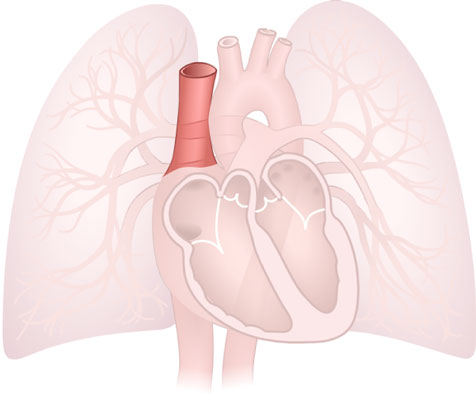
Superior Vena Cava: A large vein that delivers deoxygenated blood from the upper body into the heart.
Tricuspid Valve

Tricuspid Valve: 3-leafed valve that prevents blood from flowing backwards from the right ventricle into the right atrium.
Ventricle (Left)
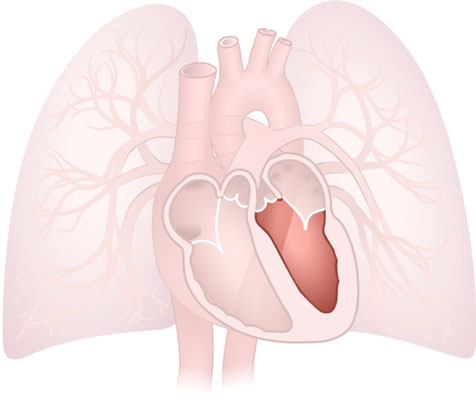
Ventricle (Left): Lower chamber of the heart that pumps oxygenated blood to the body. The left ventricle has thicker walls than the right ventricle.
Ventricle (Right)
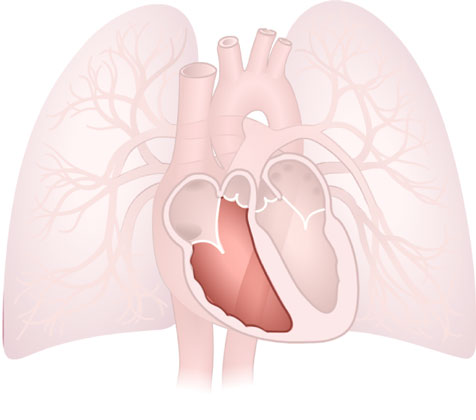
Ventricle (Right): Lower chamber of the heart that pumps deoxygenated blood into the lungs. The right ventricle has thinner walls than the left ventricle.
SHOW OUTSIDE
SHOW INSIDE
All contents copyright © 2015, University Health Network and SickKids. All rights reserved.