▼
ECG
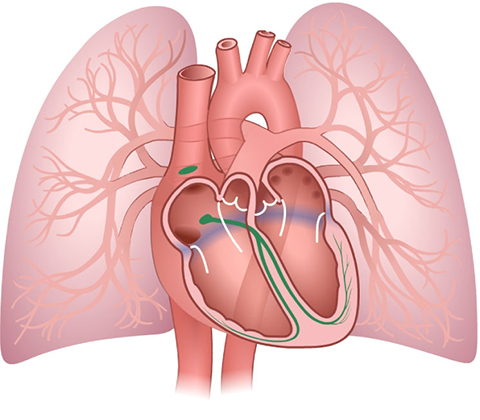
Right
Left
What is an ECG?
The letters "ECG" stand for "electro-cardiogram". An ECG is recorded by placing electrodes on the surface of the skin.
The ECG measures the electrical activity of the heart. This electrical activity controls the heart beat. Special cells called pacemakers release bursts of electrical energy which travel through the heart muscle, causing it to contract. When the muscle contracts, blood is pumped through the heart.
Select the name of the part of the heart from the list below to see a picture and a description of what it does.
Press the “View Animation” button to see animations of each step in the production of the ECG.
VIEW ANIMATION
Atrioventricular (AV) Node
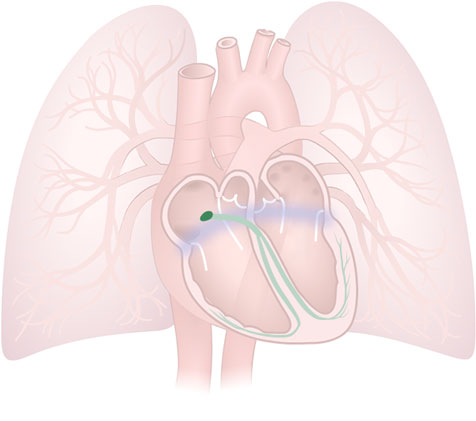
Atrioventricular (AV) Node: A group of autorhythmic (pacemaker) cells, located near the floor of the right atrium.
Bundle Branch (Left)
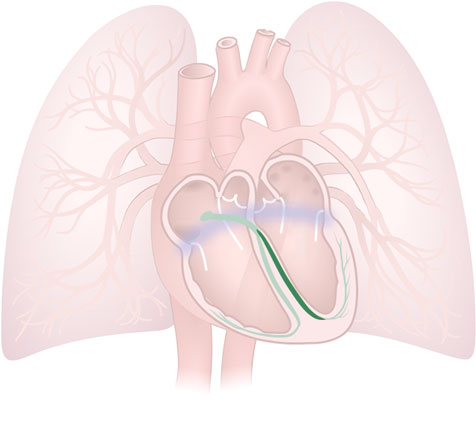
Bundle Branch (Left): A branch of the Bundle of His, that carries electrical impulses down the left side of the septum into the left ventricle.
Bundle Branch (Right)
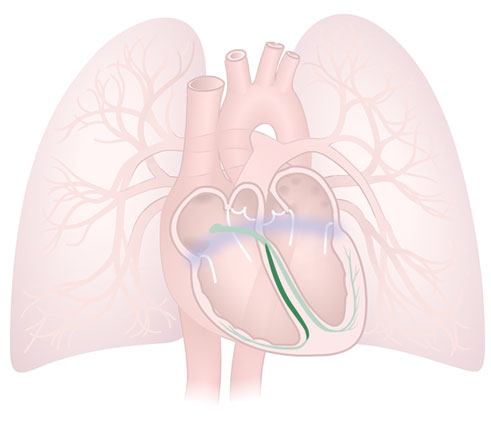
Bundle Branch (Right): A branch of the Bundle of His, that carries electrical impulses down the right side of the septum into the right ventricle.
Bundle of His
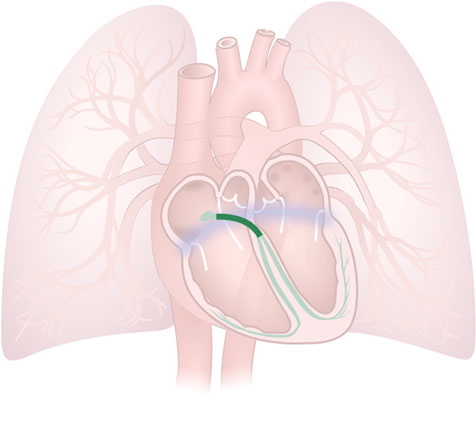
Bundle of His: A bundle of specialized muscle fibres that carry electrical impulses through the septum of the heart.
Non-Conducting Band
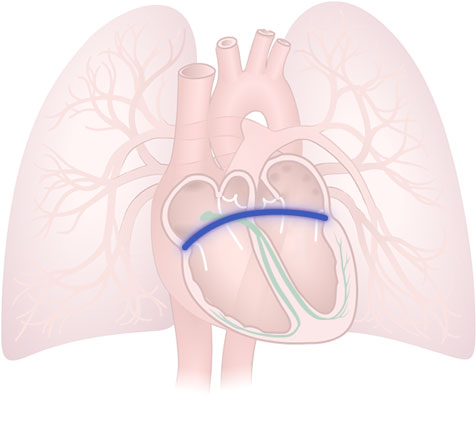
Non-Conducting Band: Fibrous ring of tissue that normally acts as an electrical insulator between the atria and the ventricles.
Sinoatrial (SA) Node
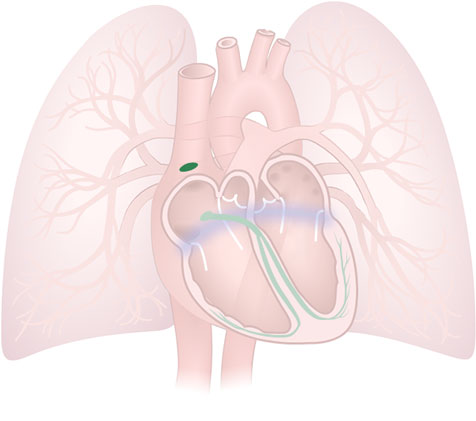
Sinoatrial (SA) Node: A group of autorhythmic (pacemaker) cells, located near the floor of the right atrium.
Purkinje Fibres
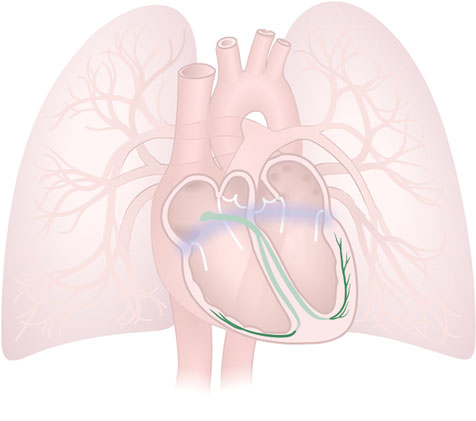
Purkinje Fibres: Specialized heart muscle fibres that rapidly conduct electrical impulses to all parts of the ventricles.
All contents copyright © 2015, University Health Network and SickKids. All rights reserved.